Recently, the deep web has appeared as a realm both intriguing and disturbing, capturing the interest of authorities, researchers, and the inquisitive alike. This concealed segment of the internet, frequently accessed through dedicated tools, features a variety of markets that operate beyond the limits of conventional society. While some view these platforms as a hub of illegal trades, others regard them as a space for freedom of expression and confidentiality, igniting a nuanced debate about liberty versus safety in the online era.
Underground markets offer a singular glimpse into an illicit economy that prospers in the underbelly. From drugs and stolen data to common items, the items traded on these venues reflect not only the wants of people seeking anonymity but also broader issues related to globalization and tech advances. As we delve into this clandestine market, we discover the intricate relationships between consumers and suppliers, the evolving methods of transaction, and the impact these markets have on the overall society.
Comprehending the Darkweb
The darkweb refers to a section of the internet that is not indexed by conventional search engines. It demands specific software, configurations, or authorization to gain entry to, making it a hidden layer that functions beneath the visible web. This secluded environment is often associated with anonymity, where users can browse and communicate without revealing their personal information. While it may house legitimate purposes, such as privacy advocacy advocacy and secure messaging for whistleblowers, it is most notorious for its involvement in criminal activities.
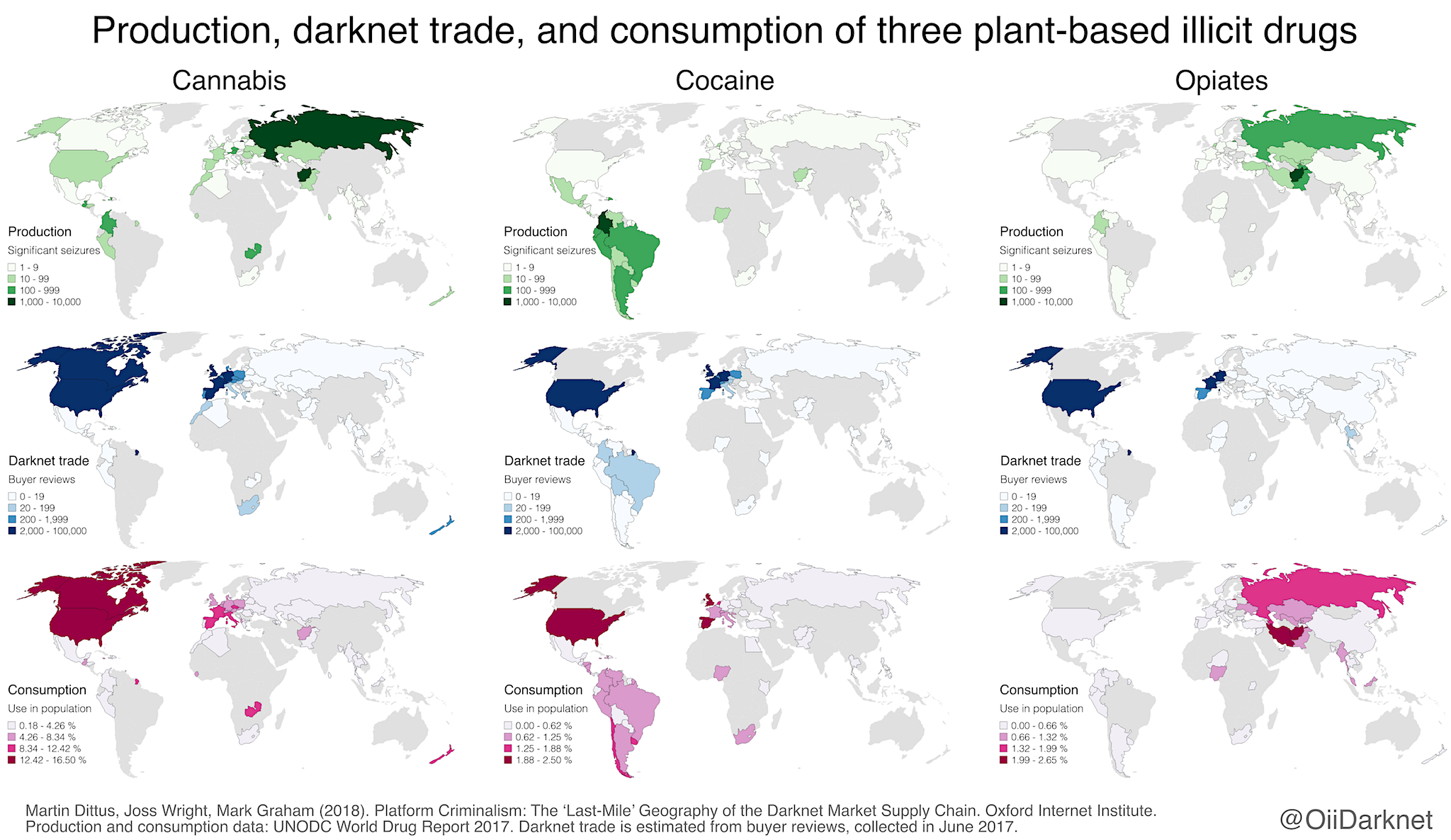
Darknet markets are online platforms within the darkweb primarily used for buying and trading illicit goods and services. These markets utilize cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to enable transactions, further ensuring user privacy. A varied range of products can be discovered here, including controlled substances, weapons, illegally obtained data, and hacking services. Each market operates under its own rules and structures, typically featuring user reviews systems to maintain some degree of reliability among buyers and sellers.
The appeal of the dark web lies in its possibility for privacy and the ability to conduct transactions free from governmental oversight. However, this identical feature contributes to the challenges it poses for authorities agencies trying to combat illegal activities. As these markets develop, they become increasingly sophisticated, utilizing advanced security measures and adjusting to opposing efforts, making it crucial for society to understand both the dark web's potential benefits and inherent dangers.
The Anatomy of Darkweb Markets
Underground markets exist as websites where forbidden products and services are exchanged, often operating under the surveillance of authorities. These marketplaces are accessible through specific software like the Tor network, which hides user actions and enhances privacy. Sellers and buyers typically interact and transact using digital currencies, additionally enhancing the secrecy of their deals. The structure is often reminiscent to traditional e-commerce websites, featuring item listings, user feedback, and ratings to establish trust among participants.
The items offered on dark web marketplaces range from drugs and fake currency to cyber tools and stolen data. Vendors often focus in specific niches, creating a rivalrous environment that lowers prices and encourages quality. Market operators frequently update their platforms to avoid discovery or closure by authorities, which can result in a continuous flux of accessible markets. This fluid nature makes it difficult for authorities to monitor and understand the full scope of these illegal ecosystems.
Moreover, the user interface on these platforms is designed to replicate legitimate online shopping, complete with search features and sorted listings. This familiarity helps attract a wide variety of participants, such as those who might not typically engage in illegal activities. Furthermore, forums and conversations within the platforms foster a sense of belonging and shared purpose, reinforcing the participation of both buyers and sellers. As a result, darkweb markets have evolved into intricate economies that operate in parallel with traditional markets, blurring the lines between lawfulness and illegality.
Issues in Governing the Dark Web
Controlling the dark web presents considerable challenges due to its inherent architecture and concealment features. The distributed nature of darkweb markets means that they are not tied to any particular jurisdiction, making it challenging for authorities agencies to apply consistent regulatory frameworks. Users and suppliers operate under pseudonyms, which complicates the recognition of people and entities involved in illicit activities. This concealment is a key appeal of dark web markets, attracting not only customers and vendors of illegal goods but also those seeking to evade surveillance and censorship.
Another challenge lies in the continuously evolving technologies that support dark web activities. As darknet markets onion address to close down certain markets or disrupt operations, alternative sites frequently arise. These new markets often adopt advanced encryption and privacy measures, making them even more difficult to trace. The swift pace of advancement in digital currencies, which serve as a major transaction method, adds another layer of difficulty. Authorities must constantly modify their strategies to keep up with these tech advancements while guaranteeing they don’t infringe on authorized users' privacy rights.
Moreover, the wide-ranging global reach of the dark web complicates global cooperation among law enforcement agencies. Different countries have diverse laws and priorities when it comes to online activities, leading to issues in working together and information sharing. This fragmentation can result in cases where dark web markets prosper in regions with lenient regulations, while enforcement efforts in other areas may yield limited results. Ultimately, without robust global collaboration and integrated legislation, efforts to regulate the dark web and break down its markets will remain substantially impeded.
